
Modern customer experiences demand AI assistants that can adapt to user preferences, including language and tone. Agentforce, Salesforce’s conversational AI, delivers just that — multilingual, tone-aware responses that feel natural and human-like.
In Agentforce, the Language setting determines the primary language and tone that the agent will use when generating responses. It affects all AI-generated conversational outputs
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- The Role of Language Settings in Agentforce
- Step by Step Guide
- Default Language and Tone
- Real Conversational Examples
- Common FAQs
- Key Difference in Control
- Key Takeaways
The Role of Language Settings in Agentforce
Language and tone settings in Agentforce form the foundation of any conversation. They determine:
- Default response language (e.g., English).
- Tone alignment (Formal, Neutral, or Casual).
- The overall personality of your AI assistant.
Why is this Important?
A well-configured language setting ensures:
- Brand alignment (formal tone for enterprises vs. casual tone for startups).
- Smooth multilingual support for global customers.
- Consistent AI responses across all touchpoints — replies, error messages, and actions.
For additional guidance, refer to Salesforce’s official documentation on AI Copilot Language and Tone
Step by Step Guide
- In Salesforce, go to Setup.
- Search for Agentforce in the Quick Find box.
- Open the Agentforce Builder.
- Within Agentforce Builder, locate the Language Settings tab.
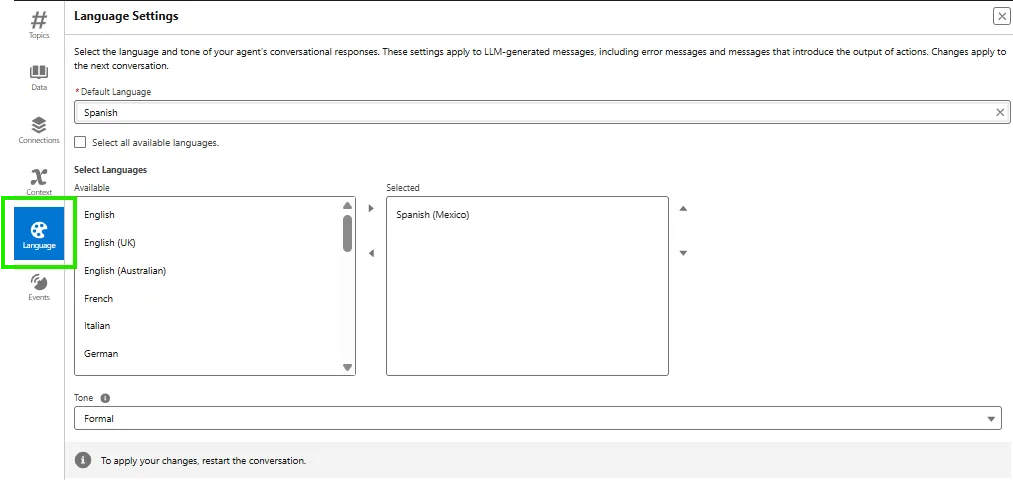
This section controls the default language and tone preferences for all conversations.
-
From the Default Language dropdown, select the language you want Agentforce to primarily use (e.g., English, Spanish, etc). This language will be used for all responses unless overridden by user input.
-
Click on Select Languages to add other supported languages. Example: Add Spanish and French if your customers interact in multiple languages. This enables auto-language detection, allowing Agentforce to switch based on the user’s input language.
-
Under Tone Control, select any one from:
- Formal ( Polished and professional )
- Neutral ( Balanced and non-evaluative )
- Casual ( Relaxed and conversational )
-
Choose a tone that matches your company’s brand style.
-
After configuring the language and tone, click Save.
-
Test the configuration in the Preview Panel of Agentforce Builder.
Default Language and Tone
If your company tone is more formal, such as used in a financial institution, you can set the language to reply in a formal tone. Conversely, if your company tone is informal, like used in a gaming company, use the casual tone and better match the overall feel of your company.
Agentforce provides three tone options:
- Formal: Professional and polished.
- Neutral: Balanced and objective.
- Casual: Friendly and relaxed.
You can also set the default language, like English or Spanish, and use “Select Languages” to allow automatic switching based on user input.
Real Conversational Examples
Let’s look at real examples where Agentforce seamlessly switched languages based on user queries.
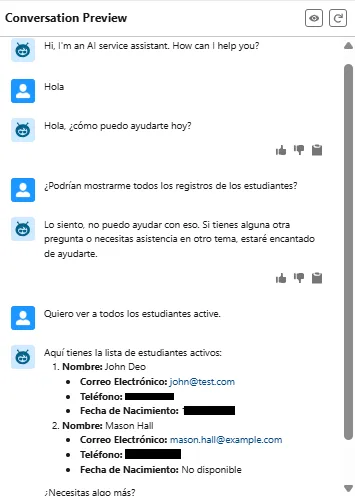
Example 1: Fetching Active Student Records
The user asks for all active students in Spanish, and Agentforce responds in Spanish while displaying a structured list.
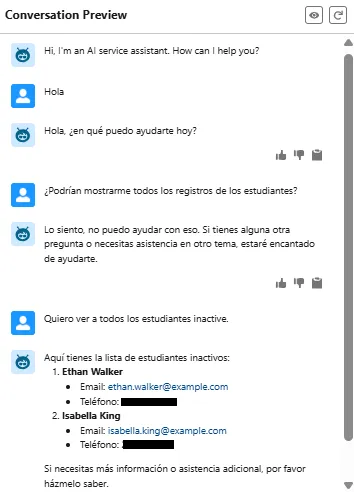
Example 2: Fetching Inactive Student Records
The user queries for inactive students. Notice how the assistant maintains Spanish responses.
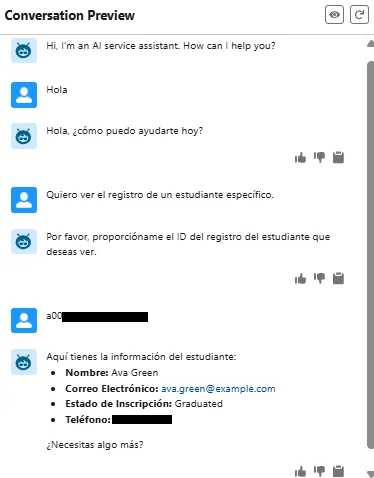
Example 3: Fetching a Specific Student Record
Agentforce asks for the student’s record ID and retrieves specific details while keeping the tone conversational.
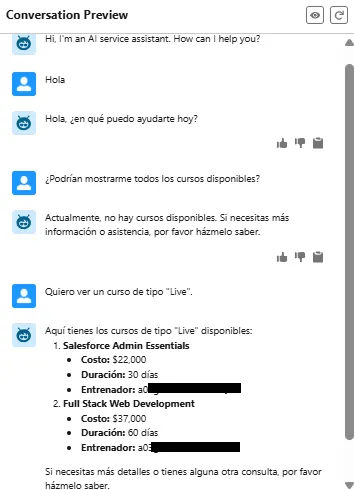
Example 4: Fetching available courses
Agentforce asks for the available courses and retrieves details of the courses while keeping the tone conversational.
Common FAQs
What’s the difference between language settings and auto-detection?
The Language setting in Agentforce and the auto-language detection by the LLM (Large Language Model) work differently and can sometimes cause confusion. Here's the key difference:
Language Setting (Agentforce UI Setting)
Purpose: This is a configuration-level setting that controls the default language and tone for all system messages and AI responses.
Function:
Ensures that error messages, action outputs, and system-generated texts are delivered in the selected default language (e.g., English, Spanish).
When you select additional languages in the "Selected Languages" list, Agentforce officially supports those languages for localized responses.
It controls UI-driven responses (like quick replies, fallback messages) rather than the free-flow conversation handled by the LLM.
Auto-Language Detection (LLM Behavior)
Purpose: The LLM (e.g., GPT in Agentforce) automatically detects the language of user input and tries to reply in the same language—even if that language is not configured in your Agentforce "Language Settings."
Function:
It's dynamic and does not depend on the UI settings.
If a user sends "¿Cómo estás?" (Spanish), the LLM may automatically reply in Spanish, even if English is the only configured language.
This behavior is part of the LLM's native multilingual capabilities, not Agentforce's settings.
Agentforce is responding with the other language if I do not select any language. WHY?
This behavior happens because Agentforce’s underlying Large Language Model (LLM) automatically detects and responds in the same language as the user input, even if you haven’t explicitly selected that language in the settings. The language selection in Agentforce guides the assistant but doesn’t strictly enforce it.
Why is Agentforce responding in another language?
-
Auto Language Detection by LLM: The LLM (e.g., GPT-powered Agentforce) automatically detects the language of the user’s input. If you send a message in Spanish, the LLM often replies in Spanish by default, even if Spanish is not selected in your configuration.
-
“Selected Languages” Setting is Not a Hard Restriction: The "Selected Languages" list in the Language Settings is primarily used for UI messages, prebuilt responses, and tone, not to enforce strict language blocking. The LLM layer still auto-adjusts its response language unless explicitly instructed not to.
-
Fallback Behavior: If the default language (e.g., English) is not enforced in the prompt or configuration, the model tries to match the user’s language, which results in this multilingual behavior.
What happens when conflicts occur?
If you set English as the default language but don’t instruct the LLM to “always respond in English,” the LLM might still switch to another language if the user uses that language.
How to Enforce Language Settings?
Use System Prompt Guardrails, like: "Always respond in English regardless of input language."
Or configure a pre-processor to translate any input into English and force the response in English.
Key Difference in Control
Language Setting = What you configure for the agent’s intended communication style.
Auto-Language Detection = What the LLM guesses based on user input (unless explicitly restricted).
Key Takeaways
- Language and tone settings shape brand voice and create better customer engagement.
- Real-world examples show how Agentforce adapts to multilingual queries.
- Error handling is essential to ensure seamless conversations.