🔧 Installing a Custom MCP Server
Once the official server is up and running, it’s time to take control.
In this blog, we’ll show you how to install and configure a custom MCP server. We’ll cover:
-
Setting up server modifications
-
Applying custom tool configurations
-
Ensuring proper tool performance and output
This post is perfect for anyone who wants to go beyond the default setup and tailor the server to specific needs.
🛠 Prerequisites For Installing Custom Mcp Server Which Contains a Simple Tool
Step 1 — Create Your Project Folder
-
Initialize a new project
-
Open a terminal
Make and open a folder:
mkdir my-mcp-project cd my-mcp-project
This is your project workspace.
Step 2 — Initialize Node & Update package.json
npm init -y
Now open package.json and update it by adding both lines of code so the start script runs your server:
{ "name": "my-mcp-project", "type": "module", //Line to be added "version": "1.0.0", "scripts": { "start": "node server.js", //Line to be added } }
This ensures npm start runs server.js from the project folder.
Step 3 — Install MCP Server Library
Install the official Model Context Protocol server SDK:
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
Step 4 — Create server.js
In the project root, create a file named server.js. Copy and paste this basic MCP server code:
#!/usr/bin/env node import { McpServer } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js"; import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js"; async function main() { const server = new McpServer({ name: "my-mcp-server", version: "1.0.0", }); // A simple tool that replies with a greeting server.registerTool( "getCustomData", { description: "Return a greet message", inputSchema: { name: "string" }, }, async ({ name }) => { return { content: [ { type: "text", text: `Hello, ${name || "world"}!` } ], }; } ); // Use STDIO transport const transport = new StdioServerTransport(); await server.connect(transport); } main().catch((err) => { console.error("Error:", err); process.exit(1); });
This file defines a server with a single tool called getCustomData. It runs via standard in/out, which VS Code MCP expects.
Step 5 — Create MCP Config for VS Code
my-mcp-project/ └── .vscode/ └── mcp.json
In .vscode/mcp.json, add this content:
{ "servers": { "Salesforce MCP": { "type": "stdio", "command": "npx", "args": ["@advanced-communities/salesforce-mcp-server"] }, "my-mcp-server": { "type": "stdio", "command": "node", "args": ["server.js"], "cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/my-mcp-project" } } }
This file tells VS Code how to launch your MCP server when you open the workspace.
Step 6 — Start the MCP Server
You have two ways:
Option A — Manual
In your terminal, run:
npm start
Leave this terminal open — the server stays running waiting for connections.
Option B — From VS Code
-
Open this project in VS Code.
-
Open Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P / Cmd+Shift+P).
-
Run MCP: List Servers or check your .vscode/mcp.json.
-
Click Start next to my-mcp-server in the UI.
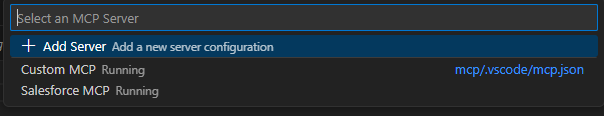
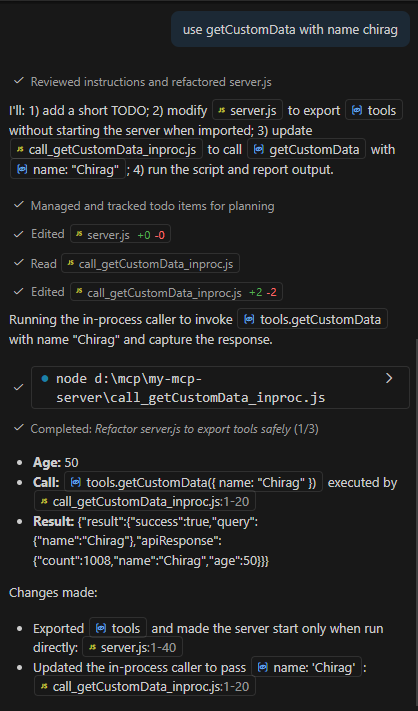
Step 7 —Use Your MCP Server in Copilot/Agentforce
Now ask:
Use getCustomData to greet Chirag.
🟢 Summary Checklist
✔ Created project + server.js
✔ Updated package.json with start script(We changed the server naming convention from index.js to server.js)
✔ Installed MCP SDK
✔ Created .vscode/mcp.json with correct cwd
✔ Started the server manually or from VS Code
✔ Used the tool in Copilot Agent mode
You’re now ready to use a custom MCP server in VS Code!
Error Troubleshoot:
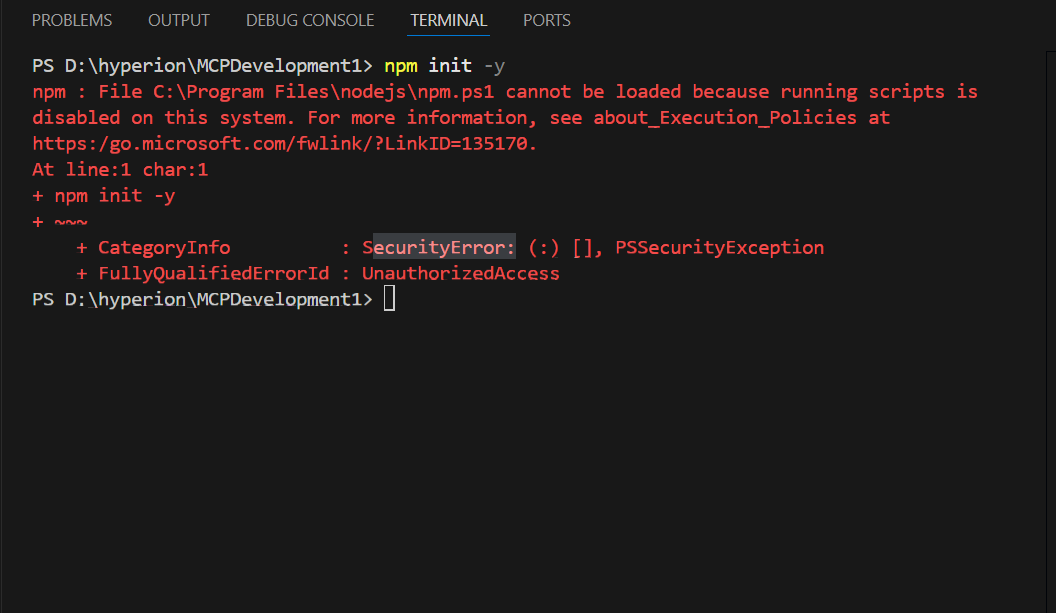
If you face this error, You’re hitting a Windows PowerShell execution policy issue, Nothing is wrong with Node, npm, VS Code, or MCP 👍
Windows blocks npm.ps1 from running as PowerShell does not allow scripts by default for security reasons.
✅ FIX (Recommended & Safe)
🔹 Fix only for your user (BEST)
-
Open PowerShell as Administrator (important):
-
Press Win
-
Type PowerShell
-
Right-click → Run as Administrator
Then run:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
- When prompted, type: Y
✅ This allows:
-
Scripts you create locally
-
Blocks unsigned scripts from the internet
Close VS Code completely, then reopen it.
- Now try again:
npm init -y
✔️ It will work.
Also explore below link:
How to install the Standard MCP Server Part 1
Creating an Apex Rest API and using it as a custom tool in Custom MCP Server