
A "global callable class" in Apex is a class marked global that implements the Callable interface. That means:
- global: it can be accessed outside your package/namespace (so external callers can use it).
- Callable: it exposes a single entry point, call(String action, Map<String, Object> args), and you route to different methods based on action.
In simple terms: it’s a single front door you can use to call multiple backend methods by name.
Utility
- Lets external systems (or tools like MCP) call Apex methods dynamically.
- You can add new “actions” without changing the interface — just add a new when branch.
- Works well for generic integrations where the caller only knows a method name + arguments.
Benefits
- One endpoint, many operations: no need to build separate REST endpoints per method.
- Flexible: can evolve without breaking callers.
- Tool‑friendly: easy for automation tools to call a single “dispatcher”.
- Centralized control: you can validate, log, and secure everything in one place.
A global class Extension which implements Callable can’t be invoked over REST by itself. You still need an API surface (Apex REST, Tooling, or a custom endpoint) that calls Extension.call().
Typical pattern:
-
Create an Apex REST class that receives action + args.
-
Inside it, instantiate Extension and call extension.call(action, args).
-
Your MCP tool calls that REST endpoint.
Here’s the code for Apex side (Callable + REST wrapper), and the MCP tool call in Node.
Apex: callable class
Extension.apxcglobal class Extension implements Callable { String concatStrings(String stringValue) { return stringValue + stringValue; } Decimal squareNumbers(Decimal decimalValue) { return decimalValue * decimalValue; } global Object call(String action, Map<String, Object> args) { switch on action { when 'concatStrings' { return this.concatStrings((String)args.get('stringValue')); } when 'squareNumbers' { return this.squareNumbers((Decimal)args.get('decimalValue')); } when else { throw new ExtensionMalformedCallException('Method not implemented'); } } } global class ExtensionMalformedCallException extends Exception {} }
Apex: REST wrapper
ExtensionCallApi.apxc@RestResource(urlMapping='/ExtensionCall/*') global with sharing class ExtensionCallApi { @HttpPost global static String callExtension() { Map<String, Object> body = (Map<String, Object>)JSON.deserializeUntyped( RestContext.request.requestBody.toString() ); String action = (String)body.get('action'); Map<String, Object> args = (Map<String, Object>)body.get('args'); Extension ext = new Extension(); Object result = ext.call(action, args == null ? new Map<String, Object>() : args); return JSON.serialize(new Map<String, Object>{ 'result' => result }); } }
MCP tool (Node)
server.jsmcpServer.registerTool( "extensionCall", { description: "Dispatches to Apex Extension.call via REST.", inputSchema: z.object({ action: z.string(), args: z.record(z.any()).optional() }) }, async ({ action, args }) => { const result = await conn.apex.post("/ExtensionCall/", { action, args: args ?? {} }); return { content: [{ type: "text", text: JSON.stringify(result) }], }; } );
Now, To call this tool, Use the MCP UI with the tool name extensionCall and pass action + args:
For Concatinate:
call extensionCall {"action":"concatStrings","args":{"stringValue":"abc"}}
For Square:
call extensionCall {"action":"squareNumbers","args":{"decimalValue":7}}
Use it from the CLI like this:
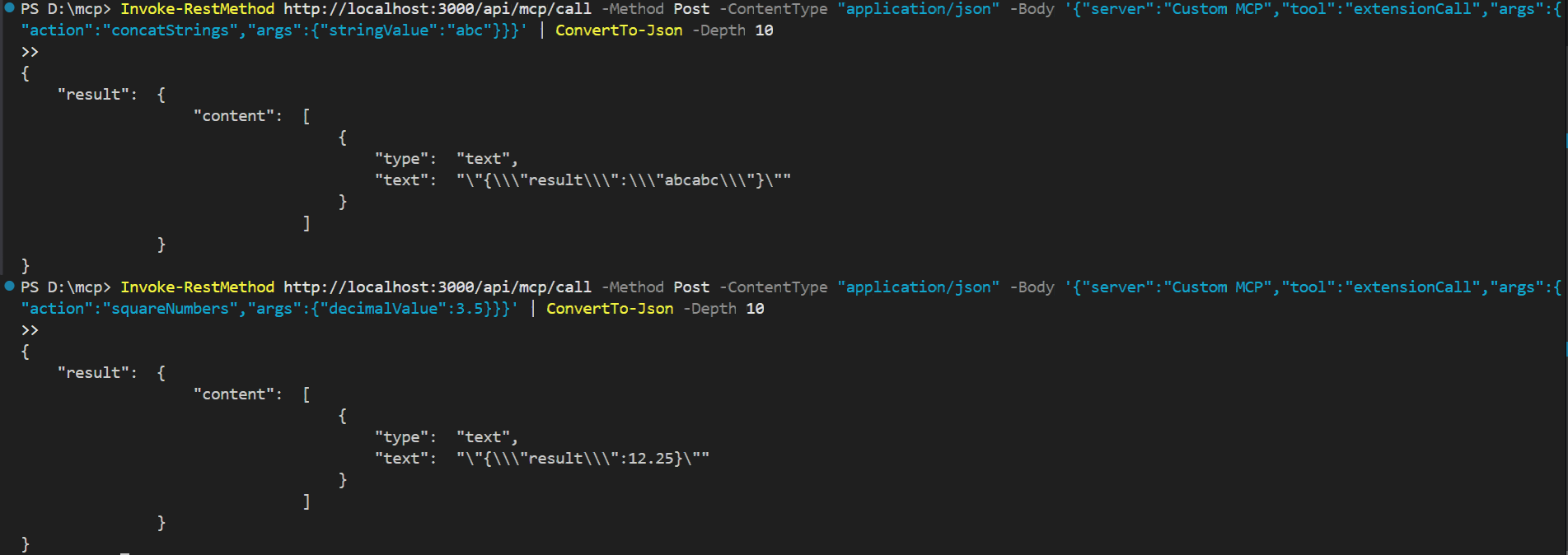
powershellInvoke-RestMethod http://localhost:3000/api/mcp/call -Method Post -ContentType "application/json" ` -Body '{"server":"Custom MCP","tool":"extensionCall","args":{"action":"concatStrings","args":{"stringValue":"abc"}}}' | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 10
For Square:
powershellInvoke-RestMethod http://localhost:3000/api/mcp/call -Method Post -ContentType "application/json" ` -Body '{"server":"Custom MCP","tool":"extensionCall","args":{"action":"squareNumbers","args":{"decimalValue":3.5}}}' | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 10
You will see the output like this:
Here’s the end‑to‑end flow for easy understanding for a UI tool call, mapped to the files/classes you have now:
1) UI sends the tool call
- Agentforce Prompt Box sends tools/call with:
{ "name": "extensionCall", "arguments": { "action": "...", "args": {...} } }
2) MCP server receives it
- Custom MCP server (server.js) receives the request over stdio.
3) Tool handler runs
-
extensionCall handler executes.
-
It calls getSfConnection() to create a jsforce.Connection.
4) MCP server calls Salesforce
- Handler sends POST to Apex REST:
/ExtensionCall/
with { action, args }.
5) Apex REST invokes Callable
-
ExtensionCallApi receives the request.
-
It instantiates Extension and calls Extension.call(action, args).
6) Result flows back
-
Apex returns JSON (e.g., { "result": 16 }).
-
Tool returns content + structuredContent. (If the result is a string, structuredContent gives error as it expects object/record only. So in that case we simply removed the structuredContent in return block)
server.jsreturn { content: [{ type: "text", text: JSON.stringify(result) }], structuredContent: result //Removed this line };
- UI renders the response.
Now, You have a Global Callable Class which contain Multiple Actions and Implements Callable Registered as a Tool in Your Custom MCP Server!